Challenge
The IBTCI Monitoring and Evaluation for the Tunisia and Libya (METAL) Activity provides technical support for the achievement of USAID’s strategy goals and development objectives in Tunisia and Libya by assisting its efforts to gain and apply knowledge derived from monitoring, evaluation, and learning (MEL). In July 2020, USAID requested that IBTCI/METAL monitor USAID/Tunisia’s COVID-19 activities, including a national media campaign to educate the public regarding COVID-19 protection measures and a COVID-19 hotline providing counseling services to individuals facing COVID-19-related challenges.
Solution
Premise engaged its data Contributor network across the 24 governorates of Tunisia to complete various COVID-19 surveys via the Premise application. The survey questionnaire was designed to gauge exposure to and intention for change of behavior as a result of specific messaging campaigns, as well as the awareness of the public hotline.
- Awareness and effectiveness of certain social media and other public service campaigns related to COVID-19
- Engagement with preventative behaviors against COVID-19
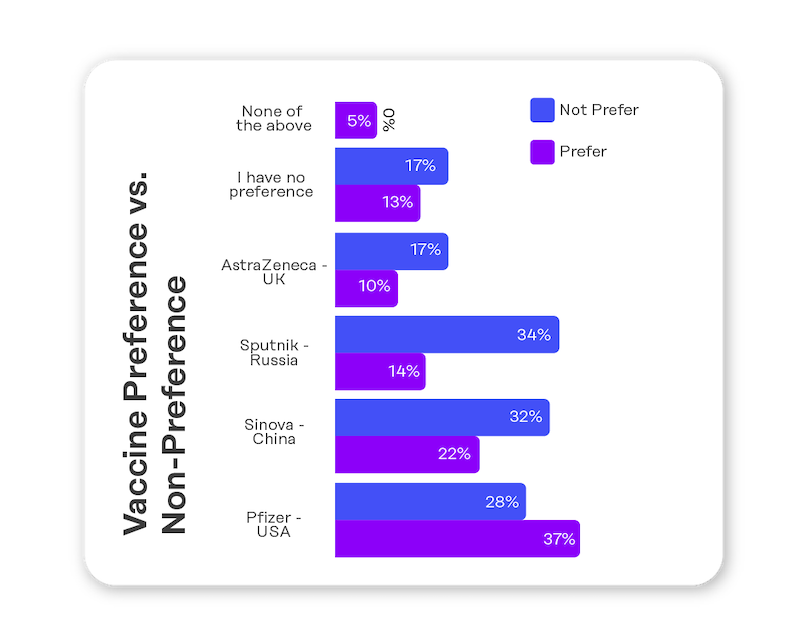
- Sentiments toward the COVID-19 vaccine
- Awareness and use of the COVID-19 hotline available throughout Tunisia
Two rounds of data were collected over the course of six months in order to observe changes over time in relation to COVID-19-related behavior and awareness. During each round of data collection, a total of 1,632 responses were collected per survey to ensure a nationally representative sample.
Findings
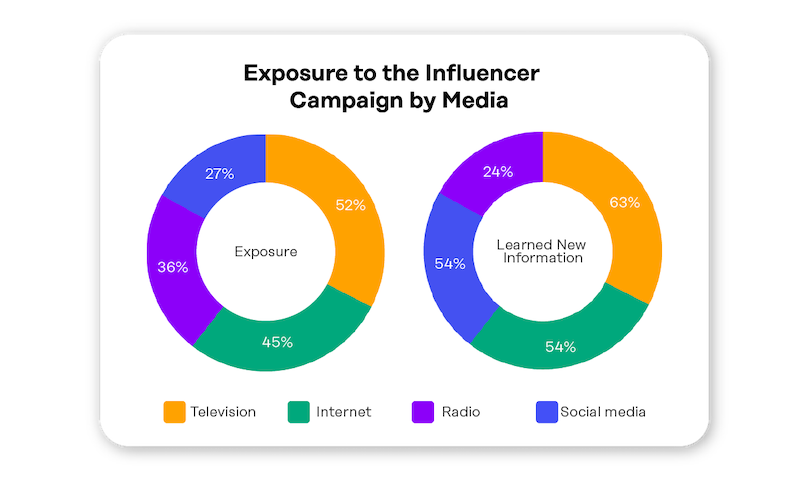
Contributor responses from the COVID-19 surveys provided valuable insights to the METAL team as they worked to assess USAID Tunisia’s COVID-19-related activities. For example, the results showed that television and internet had the highest reach for Contributors receiving public awareness messaging on COVID-19, however, social media had the biggest impact in terms of behavior change. It was also determined that celebrities and influencers have a positive effect on message receptivity. Responses also showed that while mask wearing declined precipitously between the first and second rounds of data collection, likeliness to get the vaccine increased showing a shift in protective behaviors among the general population. Vaccine type and location of origin also impacted sentiments toward receiving it.
Implications
Equipped with these observations from Premise, our partner was able to:
- Understand the most effective mediums and messengers for communicating COVID-19 awareness information
- Gain insight into differences in COVID-19 knowledge and perception by governorate, gender, and urban-rural differences for a more nuanced understanding for future areas of focus
- Better understand vaccine readiness across the country and prepare for the possible impacts of misinformation to increase public trust around